Data Structure - Circular Linked List
Circular Linked List is a variation of Linked list in which the first element points to the last element and the last element points to the first element. Both Singly Linked List and Doubly Linked List can be made into a circular linked list.
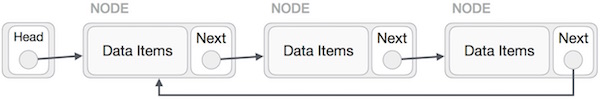
Singly Linked List as Circular
In singly linked list, the next pointer of the last node points to the first node.
Doubly Linked List as Circular
In doubly linked list, the next pointer of the last node points to the first node and the previous pointer of the first node points to the last node making the circular in both directions.
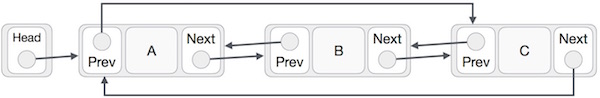
As per the above illustration, following are the important points to be considered.
The last link's next points to the first link of the list in both cases of singly as well as doubly linked list.
The first link's previous points to the last of the list in case of doubly linked list.
Basic Operations
Following are the important operations supported by a circular list.
insert − Inserts an element at the start of the list.
delete − Deletes an element from the start of the list.
display − Displays the list.
Insertion Operation
Following code demonstrates the insertion operation in a circular linked list based on single linked list.
Example
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data) {
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data= data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
Deletion Operation
Following code demonstrates the deletion operation in a circular linked list based on single linked list.
//delete first item
struct node * deleteFirst() {
//save reference to first link
struct node *tempLink = head;
if(head->next == head) {
head = NULL;
return tempLink;
}
//mark next to first link as first
head = head->next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
Display List Operation
Following code demonstrates the display list operation in a circular linked list.
//display the list
void printList() {
struct node *ptr = head;
printf("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL) {
while(ptr->next != ptr) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
printf(" ]");
}
To know about its implementation in C programming language, please click here.



