Chemistry - Combustion and Flame
Introduction
A chemical process in which a substance reacts with oxygen and give off heat is known as combustion.
The substance that undergoes combustion is called as combustible or fuel.
The fuel can be in the form of solid, liquid, or gas.
During the combustion, light is also given off either in the form of a flame or as a glow.

The substances which vaporize during burning time, give flames.
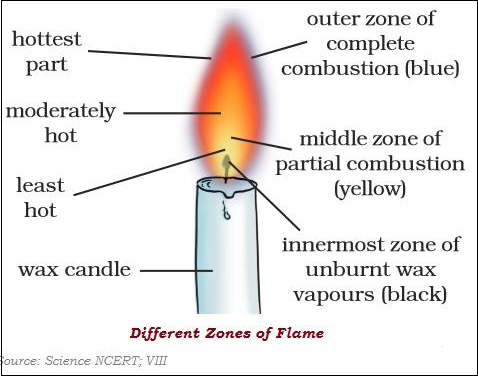
There are three different zones of a flame dark zone, luminous zone and non-luminous zone.
Different substances catch fire at different temperatures.
The lowest temperature at which a substance catches fire is known as its ignition temperature.
A match contains antimony trisulphide and potassium chlorate.
The rubbing surface of match contains powdered glass and a little red phosphorus.
Red phosphorus is much less dangerous.
When the match stick is struck against the rubbing surface, some red phosphorus gets converted into white phosphorus; the process immediately reacts with potassium chlorate present in the matchstick head and produce enough heat to ignite antimony trisulphide; likewise, combustion starts.
The substances, which have very low ignition temperature and can easily catch fire with a flame, are known as inflammable substances. E. g. petrol, alcohol, Liquified Petroleum Gas (LPG), etc.
Fire Extinguisher
Water is the most common fire extinguisher.
Water, as fire extinguisher, works only when things like wood and paper are on fire.

If electrical equipment is on fire, water may conduct electricity and damage those trying to douse the fire.
Water is also not a good extinguisher for fires involving oil and petrol.
For fires that involve electrical equipment and inflammable materials such as petrol, Carbon Dioxide (CO2) is the best extinguisher.

One of the ways to get CO2 is to release plenty of dry powder of chemicals such as sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) or potassium bicarbonate.
Phosphorus burns in air at room temperature.
The amount of heat energy produced on complete combustion of 1 kg of a fuel is known as its calorific value.
The calorific value of a fuel is measured in a unit called kilojoule per kg (kJ/kg).
The following table illustrates the Calorific Values of Different Fuels −
| Fuel | Calorific Value (kJ/kg) |
|---|---|
| Cow dung cake | 6000-8000 |
| Wood | 17000-22000 |
| Coal | 25000-33000 |
| Petrol | 45000 |
| Kerosene | 45000 |
| Diesel | 45000 |
| Methane | 50000 |
| CNG | 50000 |
| LPG | 55000 |
| Biogas | 35000-40000 |
| Hydrogen | 150000 |
Combustion of most fuels releases carbon dioxide in the environment.
Increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the air is most likely causes global warming.
The rise in temperature of the atmosphere of the earth is known as Global Warming.
Global warming causes melting of polar glaciers, which leads to a rise in the sea level that ultimately causing floods in the coastal regions.
Oxides of sulphur and nitrogen dissolve in rain water and form acids; such type of rain is known as acid rain.



