MVVM – First Application
In this chapter, we will learn how to use MVVM patterns for simple input screen and the WPF application that you may already be used to.
Let’s have a look at a simple example in which we will be using MVVM approach.
Step 1 − Create a new WPF Application project MVVMDemo.
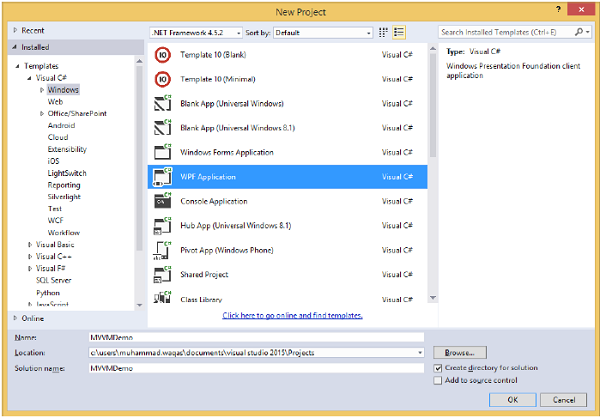
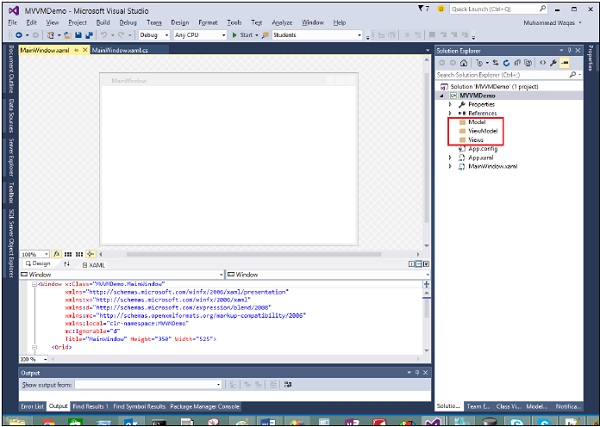
Step 2 − Add the three folders (Model, ViewModel, and Views) into your project.
Step 3 − Add a StudentModel class in the Model folder and paste the below code in that class
using System.ComponentModel;
namespace MVVMDemo.Model {
public class StudentModel {}
public class Student : INotifyPropertyChanged {
private string firstName;
private string lastName;
public string FirstName {
get {
return firstName;
}
set {
if (firstName != value) {
firstName = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("FirstName");
RaisePropertyChanged("FullName");
}
}
}
public string LastName {
get {return lastName; }
set {
if (lastName != value) {
lastName = value;
RaisePropertyChanged("LastName");
RaisePropertyChanged("FullName");
}
}
}
public string FullName {
get {
return firstName + " " + lastName;
}
}
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
private void RaisePropertyChanged(string property) {
if (PropertyChanged != null) {
PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(property));
}
}
}
}
Step 4 − Add another StudentViewModel class into ViewModel folder and paste the following code.
using MVVMDemo.Model;
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
namespace MVVMDemo.ViewModel {
public class StudentViewModel {
public ObservableCollection<Student> Students {
get;
set;
}
public void LoadStudents() {
ObservableCollection<Student> students = new ObservableCollection<Student>();
students.Add(new Student { FirstName = "Mark", LastName = "Allain" });
students.Add(new Student { FirstName = "Allen", LastName = "Brown" });
students.Add(new Student { FirstName = "Linda", LastName = "Hamerski" });
Students = students;
}
}
}
Step 5 − Add a new User Control (WPF) by right click Views folder and Select Add > New Item…
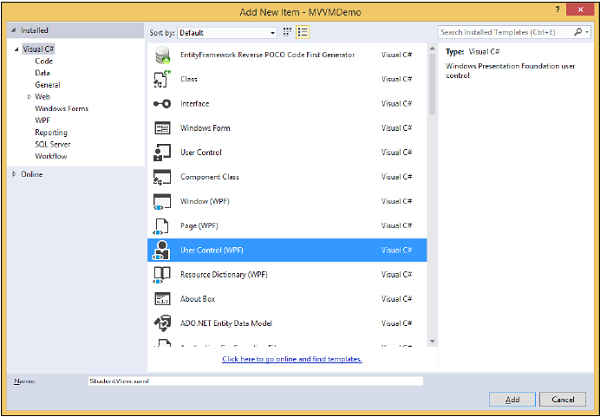
Step 6 − Click Add button. Now you will see the XAML file. Add the following code into StudentView.xaml file which contains different UI elements.
<UserControl x:Class = "MVVMDemo.Views.StudentView"
xmlns = "https://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x = "https://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:mc = "https://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:d = "https://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:local = "clr-namespace:MVVMDemo.Views"
mc:Ignorable = "d"
d:DesignHeight = "300" d:DesignWidth = "300">
<Grid>
<StackPanel HorizontalAlignment = "Left">
<ItemsControl ItemsSource = "{Binding Path = Students}">
<ItemsControl.ItemTemplate>
<DataTemplate>
<StackPanel Orientation = "Horizontal">
<TextBox Text = "{Binding Path = FirstName, Mode = TwoWay}"
Width = "100" Margin = "3 5 3 5"/>
<TextBox Text = "{Binding Path = LastName, Mode = TwoWay}"
Width = "100" Margin = "0 5 3 5"/>
<TextBlock Text = "{Binding Path = FullName, Mode = OneWay}"
Margin = "0 5 3 5"/>
</StackPanel>
</DataTemplate>
</ItemsControl.ItemTemplate>
</ItemsControl>
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
</UserControl>
Step 7 − Now add the StudentView into your MainPage.xaml file using the following code.
<Window x:Class = "MVVMDemo.MainWindow"
xmlns = "https://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x = "https://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d = "https://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc = "https://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local = "clr-namespace:MVVMDemo"
xmlns:views = "clr-namespace:MVVMDemo.Views"
mc:Ignorable = "d"
Title = "MainWindow" Height = "350" Width = "525">
<Grid>
<views:StudentView x:Name = "StudentViewControl" Loaded = "StudentViewControl_Loaded"/>
</Grid>
</Window>
Step 8 − Here is the implementation for Loaded event in the MainPage.xaml.cs file, which will update the View from the ViewModel.
using System.Windows;
namespace MVVMDemo {
/// <summary>
/// Interaction logic for MainWindow.xaml
/// </summary>
public partial class MainWindow : Window {
public MainWindow() {
InitializeComponent();
}
private void StudentViewControl_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) {
MVVMDemo.ViewModel.StudentViewModel studentViewModelObject =
new MVVMDemo.ViewModel.StudentViewModel();
studentViewModelObject.LoadStudents();
StudentViewControl.DataContext = studentViewModelObject;
}
}
}
Step 9 − When the above code is compiled and executed, you will receive the following output on your main window.
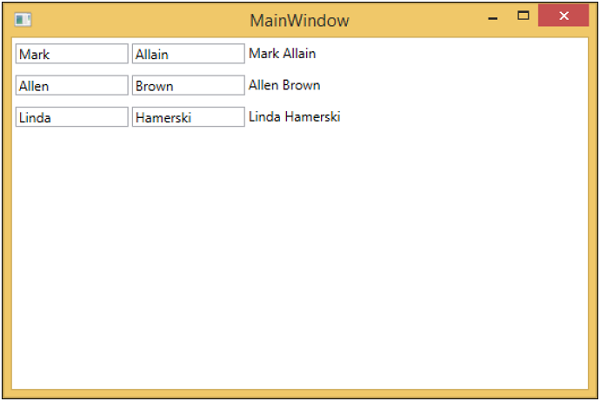
We recommend you to execute the above example in a step-by-step manner for better understanding.



