Wave Optics - Young's Experiment
Description:
It was carried out in 1802 by the English scientist Thomas Young to prove the wave nature of light.
Two slits S1 and S2 are made in an opaque screen, parallel and very close to each other. These two are illuminated by another narrow slit S and light falls on both S1 and S2 which behave like coherent sources.
Note that the coherent sources are derived from the same sources. In this way, any phase which occurs in S will occur in both S1 and S2. The phase difference (∅1 - ∅2) between S1 and S2 is unaffected and remains constant.
Light now spreads out from both S1 and S2 and falls on a screen. It is essential that the waves from the two sources overlap on the same part of the screen. If one screen is covered up, the other produces a wide smoothly illuminated patch on the screen. But when both slits are open there is formation of interference fringes.
Where,
Φ = Phase difference
I = Resultant intensity
I1,I2 = Intensity of individual waves.
Condition for bright fringes or maxima:
Φ = 2nΠ or p = nλ path difference
Where,
n = 0, 1, 2, …………
Condition for dark fringes or minima:
Φ = (2n - 1)Π or p = [n - 1/2]λ, path difference
where,
n = 1, 2, 3, …………
The relation between phase difference (Φ) and the path difference (p) is given by
How to find the position of the nth Maxima or Minima on the screen?
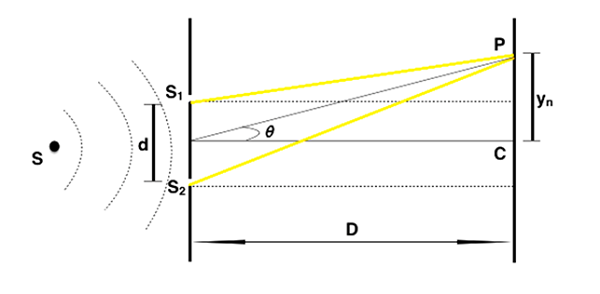
Let P be the position of the nth Maxima on the screen. The two waves arriving at P follow the path S1P and S2P, thus the path difference between the two waves is
p = S1P - S2P = dsinθ
From experimental conditions, we know that D >> d, therefore, the angle θ is small,
sinθ = tanθ = Yn/D
Thus,
p = dsinθ = dtanθ = d(Yn/D) ⇒ Yn = pD/d
For nth maxima,
p = nλ
For nth minima
p = (n - 1/2)λ
Note − The nth minima comes before the nth maxima.

