De-Brogle's Hypothess and Matter Wave
Description:
De Broglie suggested that, if radiation has both the wave nature and particle nature, then matter must also have 2 natures. He believed that energy and matter must have some symmetrical character.
De Broglie’s hypothesis says that, when a material is in motion, sometime it acts as a matter and sometimes it acts as a wave i.e. when a matter moves it is always surrounded by or guided by a wave and this wave is known as matter-wave.
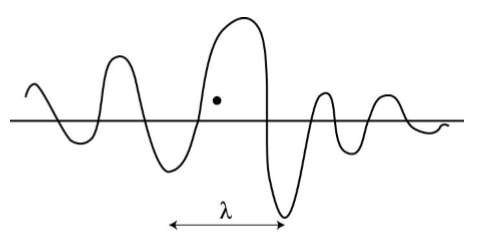
In matter wave position and momentum of matter is uncertain and it is given by uncertainty principle.
De Broglie gave the wavelength associated with a particle of mass m moving with speed v which is known as De Broglie’s wavelength and is given by −
λ = h/p = h/mv .....(1)
Where,
h = Planck’s constant.
p = Momentum.
Wavelength of matter wave ranges from zero to infinity.
Observations
If v = 0, then λ → ∞
This implies that, matter waves are associated with material only if they are moving.
If V → ∞, then λ = 0
This implies that, when velocity is very fast it appears to move in straight line as wavelength is zero.
Relation of De Broglie’s wavelength with temperature
Kinetic energy of a gas particle is given by −
K.E. = 3/2 K T
Where,
K = Boltzmann constant.
T = Absolute temperature.
As we know,
K.E. = 1/2 mv2
∴ 1/2 mv2 = 3/2 K T
Multiplying both sides by m, we get −
m2v2 = 3 m K T
∴ mv = √3 m K T
We have De Broglie’s wavelength −
λ = h/mv
Putting the value of m v −
λ = h/√3 m K T

