Capacitance
Description:
Capacitance can be understood more clearly, with the help of an analogy. Let there be two tanks T1 and T2 where T1 is a narrow tank as compared to T2. Let each tank T1 and T2 contains 5 litres of water. The level of water in both the tanks reaches as 5 cm and 2 cm respectively.
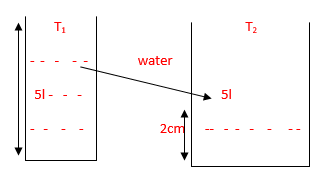
Direction of F low (T1 – T2)
height of water in (T1 > T2)
i.e T1 requires 1 litre of water to raise 1cm whereas T2 requires 2.5 litre to reach the same height. The total amount of water that can be stored in a tank is the capacity of the tank, whereas the amount of water requited to raise the level by a unit length is its capacitance.
If tanks are connected together, then, even though the volume of water in T2 is more than in T1, still water will flow from tank T1 to T2 as the height of water in T1 is greater than in T2. So, height of water within the tank is the deciding criteria for the direction of flow. The flow will stop when water level of both the tank becomes equal.
Similarly, potential of a conductor is the deciding criteria for direction of flow of charges.
Potential − Potential of a conductor is the total amount of work done in moving a unit charge within conductor.
Let there be two conducting metals (M1 and M2), each consist of 5 coulomb of charge. Let the potential of metals due to theses charges be 5V and 2V respectively.
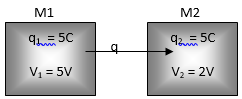
For metal M1:
For 5 volt raise in potential, charge required = 5 coulomb
So, For 1 volt raise in potential, charge required = 1 coulomb
For metal M2:
For 2 volt raise in potential, charge required = 5 coulomb
so For 1 volt raise in potential, charge required = 2.5 coulomb
So the ratio of charge required to raise the potential of metals M1 and M2 respectively by unit volt is 1: 2.5
Similarly, if there is a metal, which is given charge ‘q’ to raise the potential by ‘V’ volts
Then, for 1 volt raise in potential, charge required = q/v coulomb
This amount of charge is the capacitance of metal.
Capacitance
Capacitance of a conductor is amount to a charge required to raise its potential by 1 volt. It is symbolized by C.
C = q/v
If potential is 1 in that case C=q
Unit of capacitance
- SI unit is Farad (f).
- Practical unit is micro Farad (μf).
- 1 μf = 10-6f
1 Farad
1 farad is the capacitance of that capacitor, whose potential is raised by 1 volt when charge of 1 coulomb is given to it.
1 farade = 1coulomb/1 volt

