V at Equatorial Line Transversal
Description:
To calculate potential created by a dipole on the equatorial or transversal line, take a dipole having charges –q and +q.
Direction of electric field on the equatorial line of the dipole
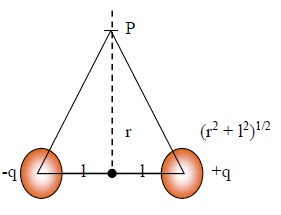
All the measurement of distances are to be taken from the centre(O). Which is the mid point of the dipole
Let the distance between O to +q and O to –q be ‘l’. So, total length between +q and –q will be ‘2l’.
Take a point ‘p’ on the equatorial line at the distance ‘r’ from the centre of the dipole as shown in figure..
To calculate potential at point ‘P’ due to the two point charges of dipole.
By using the formula for potential due to point charge,
potential due to +q , V+q = q4πε0 1(r2+12)1/2.....(1)
Since, by Pythagoras theorem the distance between P and +q is (r2 + 12)1/2
potential due to -q ,V-q = - q4πε0 1(r2+12)1/2
(potential due to +q will be positive and potential due to- q will be negative)
So, the net potential V = V1+V2
V = q4πε0 1(r2 + 12)1/2 - q4πε0 1(r2+12)1/2
V = 0
Potential at any point on the equatorial line of a dipole is 0.
Note
For point on equatorial, potential is zero but electric field is not zero.

