Motion in 1-D Fundamentals - Acceleration
Description:
Definition
Rate of change of velocity w.r.t. to time is called Acceleration.
Average Acceleration = Change in VelocityTotal time = Δv→Δt = vf - vitf - ti
Where,
‘Δv→’ is the change in velocity,
‘Δt’ is the time taken
Instantaneous Acceleration = limΔ t→0 Δv→Δt = dv→dt
Acceleration is a vector quantity. (Velocity is a Vector)
Acceleration can be either positive or negative.
Example Problem
The Position of an object moving along X - axis is given by −
x = 4 + 5t2 - 2t3
Calculate the following −
- Velocity at t = 0s and t = 2s.
- Acceleration at t = 0s and t = 2s.
- Average Acceleration between t = 0s and t = 2s
Solution
x = 4 + 5t2 - 2t3
Therefore,
v = dxdt = 10t - 6t2
a = dvdt = 10 - 12t
Velocity at t = 0s and t = 2s −
(v)t=0 = (10t - 6t2)t=0 = 0 m/s
(v)t=2 = (10t - 6t2)t=2 = -4 m/s
Acceleration at t = 0s and t = 2s −
(a)t=0 = (10 - 12t)t=0 = 10 m/s2
(a)t=2 = (10 - 12t)t=2 = -12 m/s2
Average Acceleration between t = 0s and t = 2s −
Average Acceleration = vf - vitf - ti = (v)t=2 - (v)t=02 - 0
Average Acceleration = (-12) - (10)2 = -11 m/s2
Important Points
When velocity and acceleration have the same direction (or same sign), magnitude of velocity increases. Object speeds up.
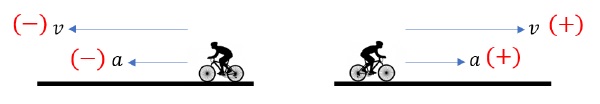
When velocity and acceleration have opposite directions (or opposite signs), the magnitude of velocity decreases. Object slows down.
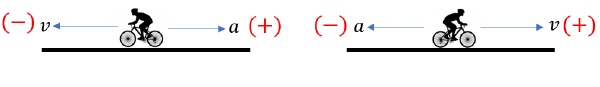
This is phenomenon of slowing down is called Retardation. Also, it should never be confused with negative acceleration.

