Problem 12 on Motion in a Straight Line
Description:
Problem
On a long horizontally moving belt, a child runs to-and-fro with a speed of 9 km/h (with respect to the belt) between his father and mother located 50 m apart on the moving belt. The belt moves with a speed of 4 km/h. For an observer on a stationary platform outside, what is the,
- Speed of the child running in the direction of motion of the belt?
- Speed of child running opposite to the direction of motion of the belt?
- Time taken by the child in first two problems?
Which answers alter if motion is viewed by one of the parents?
Solution
Velocity of child with respect to belt is referred to as, v→CB.
Velocity of child with respect to ground is referred to as, v→C.
Velocity of belt with respect to ground is referred to as, v→B.
Now,
Solving each part of the problem,
Part 1 – Child running in the direction of belt’s motion
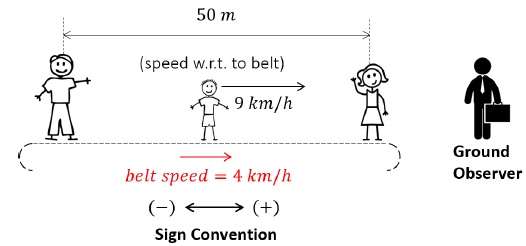
Using the concept of relative velocity, (Sign convention taken into account)
vCB = vc - vB
9 = vc - 4
vc = 13 km/h
Part 2 – Child running opposite to direction of belt’s motion
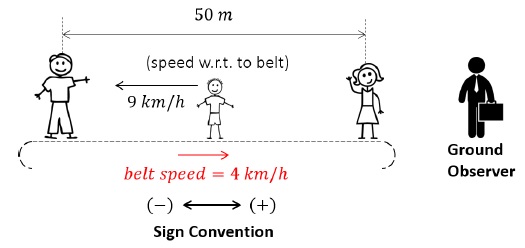
Using the concept of relative velocity,
vCB = vC - vB
-9 = vC - 4
vC = -5 km/h
Part 3(a) – Time taken by child in Part 1
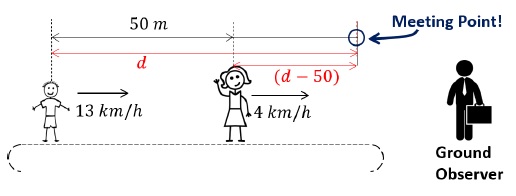
Above diagram is perceived by the ground frame observer.
The parent (mother in this case) will have a velocity of +4 km/h with respect to ground observer because she is standing stationary on the belt, which itself is moving at a velocity of +4 km/h.
Velocity of child with respect to ground observer is perceived to be +13 km/h (See Part 1).
The meeting point will be somewhere on the right of the of both parent and child as shown in the figure.
Initial separation between parent and the child = 50 m
Let the child travel a distance of ‘d’ metres.
The distance travelled by mother = (d − 50) metres [See figure]
Time taken to reach the meeting point is, ‘t’. (same for both parent and child)
Therefore, equation for the parent (mother),
(d - 50)/1000 = 4 × t
equation for the child,
(d/1000) = 13 × t
Eliminating ‘d’,
13t = (501000) + 4t
t = 509 × 1000 = 5.551000h = 19.98 s
Hence, total time elapsed in this case is, t = 19.98 s
Part 3(b) – Time taken by child in Part 2
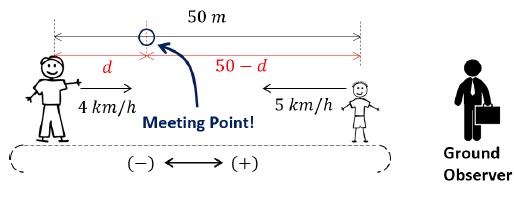
Above diagram is perceived by the ground frame observer.
The parent (father in this case) will have a velocity of +4 km/h with respect to ground observer because he is standing stationary on the belt, which itself is moving at a velocity of +4 km/h.
Velocity of child with respect to ground observer is perceived to be −5 km/h (See Part 2).
The meeting point will be somewhere on the right of the of the parent and left of the child as shown in the figure.
Initial separation between parent and the child = 50 m
Let the parent (father) travel a distance of ‘d’ metres.
The distance travelled by child = (50 − d) metres [See figure]
Time taken to reach the meeting point is, ‘t’. (same for both parent and child)
Therefore, equation for the parent (father),
d/1000 = 4 × t
equation for the child,
(50 - d)/1000 = 5 × t
Eliminating ‘d’,
4t = 501000 - 5t
t = 509 × 1000 = 5.551000h = 19.98 s
Hence, total time elapsed in this case is also, t = 19.98 s
When motion of the child is observed with respect to parents
Parents are at rest with respect to the conveyor belt.
Hence, they will perceive the velocity of child as 9 km/h, which is simply his velocity w.r.t. to belt.
Total time taken by the child to move between parents won’t change.
t = Separation of Parents on the beltVelocity of child w.r.t to belt = (50/1000)9 = 5.551000h = 19.98 s

