Motion in 1-D Fundamentals - Velocity
Description:
Rate of change of displacement w.r.t. to time is called Velocity.
- Average Velocity = Total displacementTotal time taken = Δx→Δt
- Instantaneous Velocity = limΔ t→0 Δx→Δt = dx→dt
Magnitude of Instantaneous Velocity is equal to Instantaneous Speed.
- For very small displacement, |displacement→| = distance
- Hence, |displacement→|time = distancetime
Velocity is a vector quantity. (Velocity can be either positive or negative.
Example Problem
A cyclist moves 20 m towards East from origin O. He then reverses his direction and moves 10 m. Total time taken for the entire motion is 20 s. Comment on the Average Speed and Average Velocity of the cyclist.
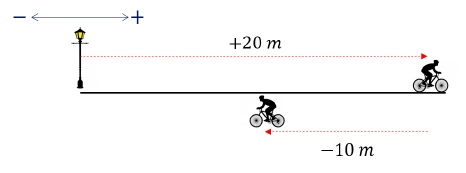
Solution
Total Displacement = 20 - 10 = +10 m
Total Distance = 20 + 10 = 30 m
Total time = 20 s
Therefore,
Average Speed = Total DistanceTotal time = 3020 = 1.5 m/s
Average Velocity = Total DisplacementTotal time = 1020 = +0.5 m/s

