Problem 3 on Motion in a Straight Line
Description:
Problem
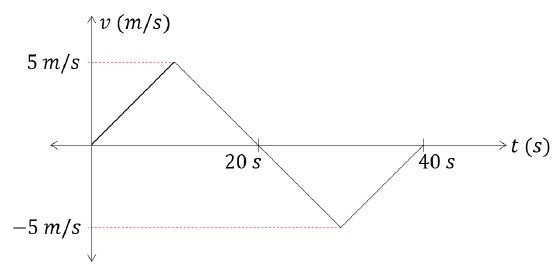
From the velocity – time graph shown below, find the distance travelled by the particle during first 40 seconds. Also find the average velocity during this period.
Solution
Let’s analyze the graph first.
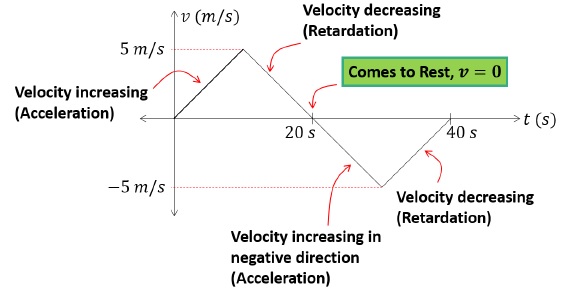
For the first segment (t = 0s to t = 10s)
- Slope of the line is positive.
- Velocity is increasing w.r.t to time. This indicates acceleration.
For the second segment (t = 10s to t = 20s)
- Slope of the line is negative.
- Velocity is decreasing w.r.t to time. This indicates retardation.
For the third segment (t = 20s to t = 30s)
Slope of the line is negative.
Velocity is increasing w.r.t. to time. This indicates acceleration in the opposite direction.
(IMPORTANT: Negative acceleration is NOT same as retardation)
For the fourth segment (t = 30s to t = 40s)
- Slope of the line is positive.
- Velocity is decreasing w.r.t. to time. This indicates retardation.
Calculating Distance and Average Velocity
Area under the curve of a v − t graph gives displacement.
Therefore,
Displacement between t = 0 s to t = 20 s,
Area under the curve = 12 × 5 × 20 = 50 m
Displacement between t = 20 s to t = 40 s,
Area under the curve = 12 × (-5) × (40 - 20) = -50 m
Now, total distance covered is the sum of magnitudes of both the displacements. (Because distance simply indicates the length of the path travelled)
Total Distance = |50| + |(-50)| = 100 m
We know that,
Average Velocity = Total displacementTotal time = 50 - 5040 = 0 m/s

