Turning Of Light In Refraction
Description:
When a light ray enters a medium its velocity and direction changes.
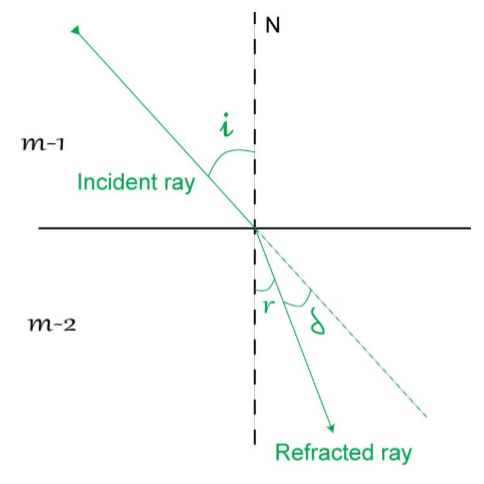
Consider a ray of light moving from medium-1 to medium 2. The light ray is not perpendicular to the interface of the two media.
When the light enters medium-2 it does not follow its original path instead it changes it direction and it deviated from its original path.
Note − If the incident ray is perpendicular/normal to the interface then it will move straight without deviation.
The angle between the incident ray and normal is known as angle of incidence.
The angle between the refracted ray and normal is known as angle of refraction.
The angle between the refracted ray and original path of ray is known as angle of deviation.
Rules for deviation
Rarer to denser
If the refractive index of refracting medium is more than the refractive index of incident medium i.e. when light is moving from rarer to denser medium there is a decrease in the velocity of ray and the refracted ray bends towards normal.
μ2 > μ1
Example: When the light is moving from water to glass.
Denser to rarer
If the refractive index of refracting medium is less than the refractive index of incident medium i.e. when light is moving from denser to rarer medium there is an increase in the velocity of ray and the refracted ray bends away from the normal.
μ2 < μ1
Example: When the light is moving from glass to water.

