Eukaryotes - Plastids
Description:
Plastids are found in all plant cells and in euglenoides. They bear specific colours hence impart specific colours to the plants parts. Based on the type of pigments plastids are classified into −
- Chloroplast
- Chromoplast
- Leucoplast
Chloroplast
Contain chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments.
These pigments are responsible for trapping light energy essential for photosynthesis.
Chloroplasts are found in the mesophyll cells of the leaves which are lens-shaped, oval, spherical, discoid organelles.
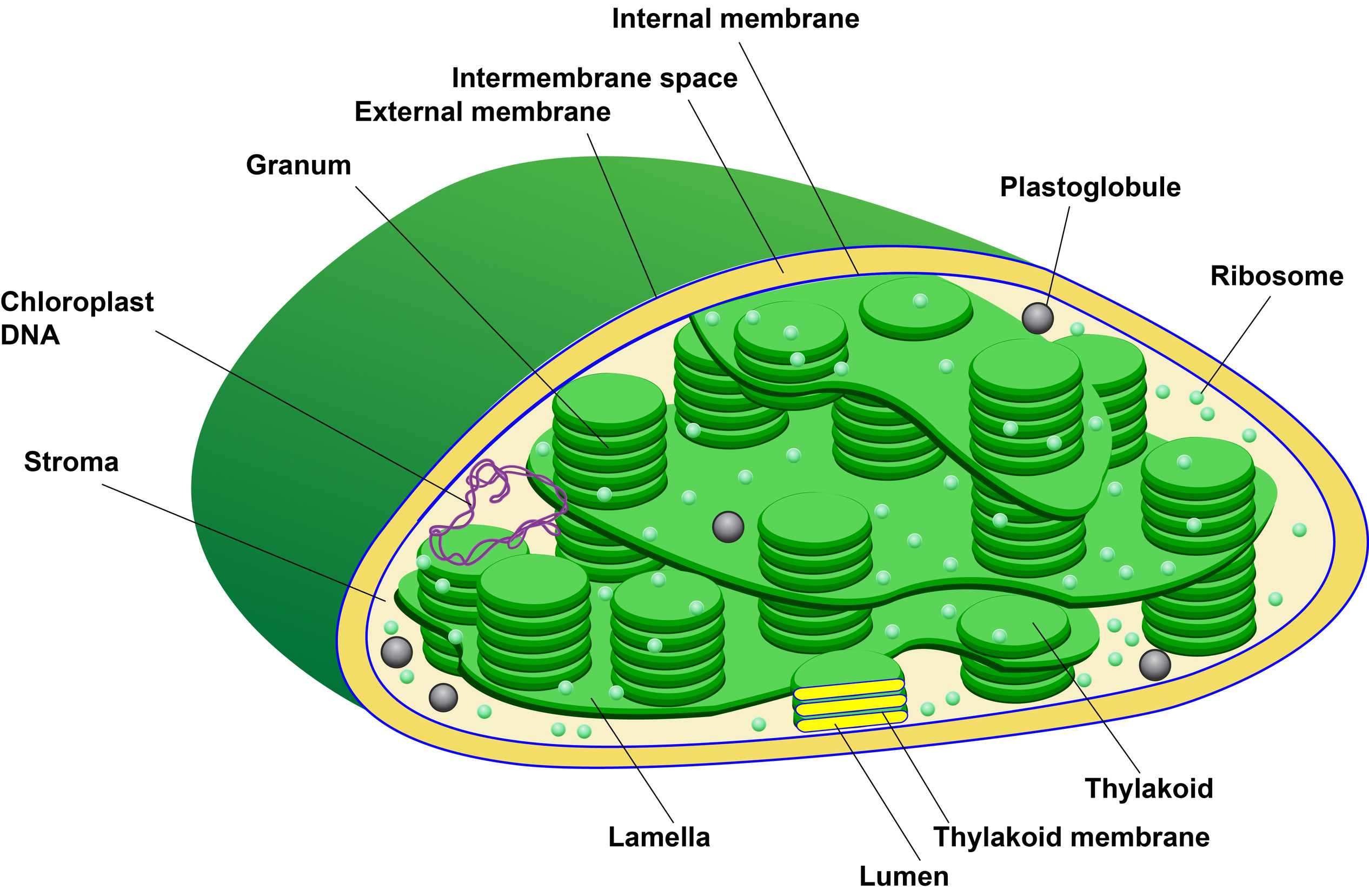
Chloroplast Structure
Chloroplast are double membrane bound structures.
The dense colourless and granular structure present inside the inner plastidial membrane is called stroma. It contains enzymes required for the synthesis of carbohydrates and proteins. It also contains small, double stranded circular DNA molecules and ribosomes.
A number of organized flattened membranous sacs are present in the stroma. They are known as thylakoids.
The thylakoids are present in the stacks which are called grana.
The chloroplast ribosomes are 70S.
Chromoplast
- Presence of fat soluble carotenoid pigments like carotene, xanthophylls etc.
- Chromoplast gives the plants colours like yellow, orange or red.
Leucoplast
- Colourless plastids of various shapes and size.
- Stored with nutrients.
- Amyloplasts store carbohydrates, elaioplast store oils and aleuroplasts store proteins.

