Meiosis I - Prophase I
Advertisements
Description:
Prophase I is the first phase of Meiosis I. This phase is more complicated and prolonged as compared to the similar stage of mitosis.
Prophase I is divided into five sub-phases: leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene and diakinesis. Another sub-phase called preleptonema is sometimes recognized prior to leptonema.
Chromosomes are not distinguishable because of their thinness. Sex chromosomes are often seen in heterochromatic bodies.
The changes a cell undergoes during the following stages are −
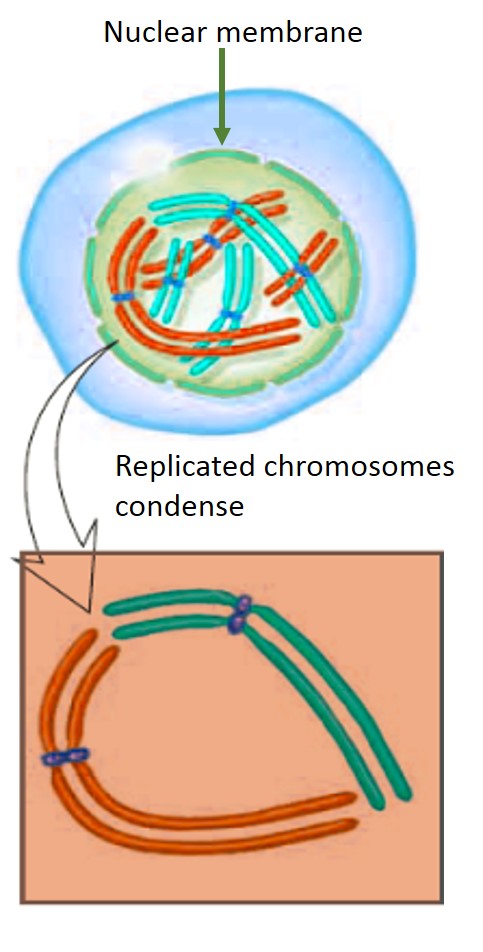
Leptotene
- Also called thin-threaded stage.
- Volume of nucleus increases.
- Formation of aster.
- Condensation of nuclear chromatin by dehydration.
- Chromosome appears long thread like and made of two sister chromatids.
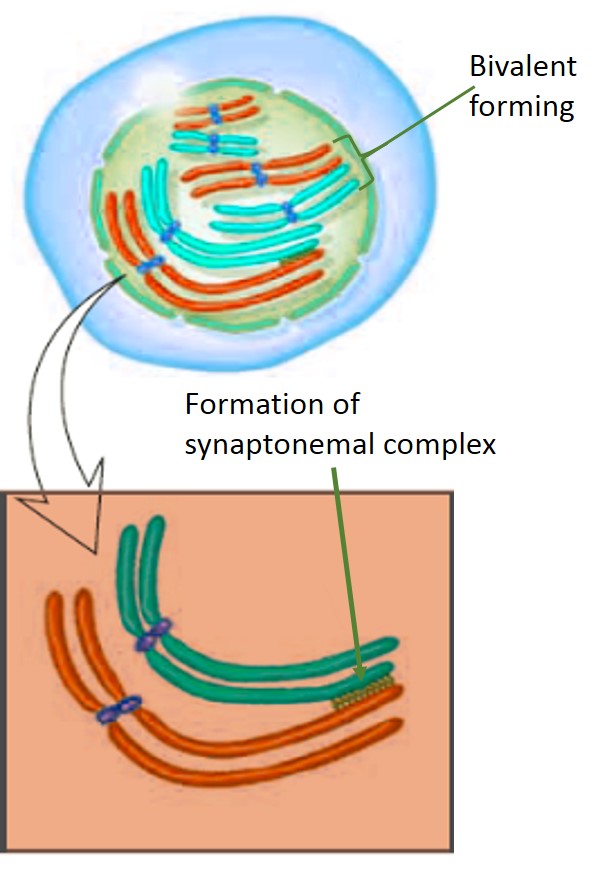
Zygotene
- Also called yoked-threaded stage.
- Pairing of homologous chromosomes occurs. This is called synapsis or syndesis.
- Formation of bivalents.
- Pairing of homologous chromosomes in a zipper-fashion.
Pachytene
- Also called thick-threaded stage.
- Further condensation of chromosomes.
- Sister chromatids are visible which are joined at the centromere and is known as dyad.
- Crossing over occurs between two non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
- Crossing over is regulated by recombinase enzyme.

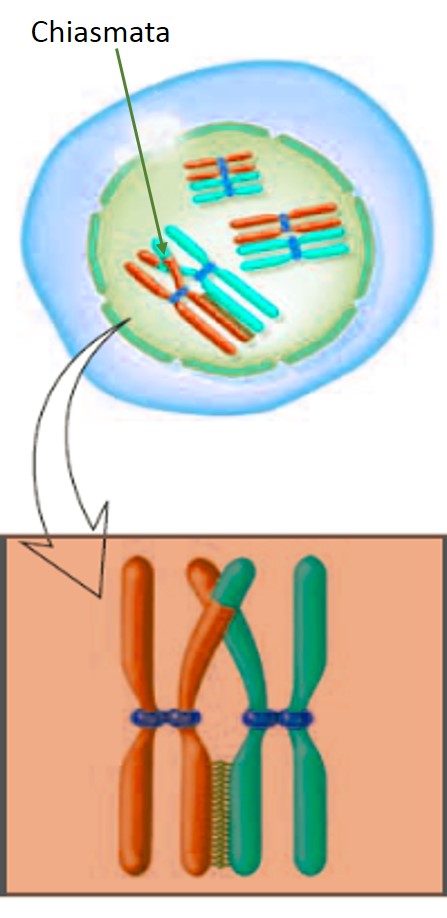
Diplotene
- Called double threaded stage.
- Longest duration.
- Nuclear membrane and nucleoli start disappearing.
- The homologous chromosomes start separating.
- The point of attachment or crossing over is known as chiasmata.
- The chiasmata starts moving towards the ends of chromosomes called terminalisation.
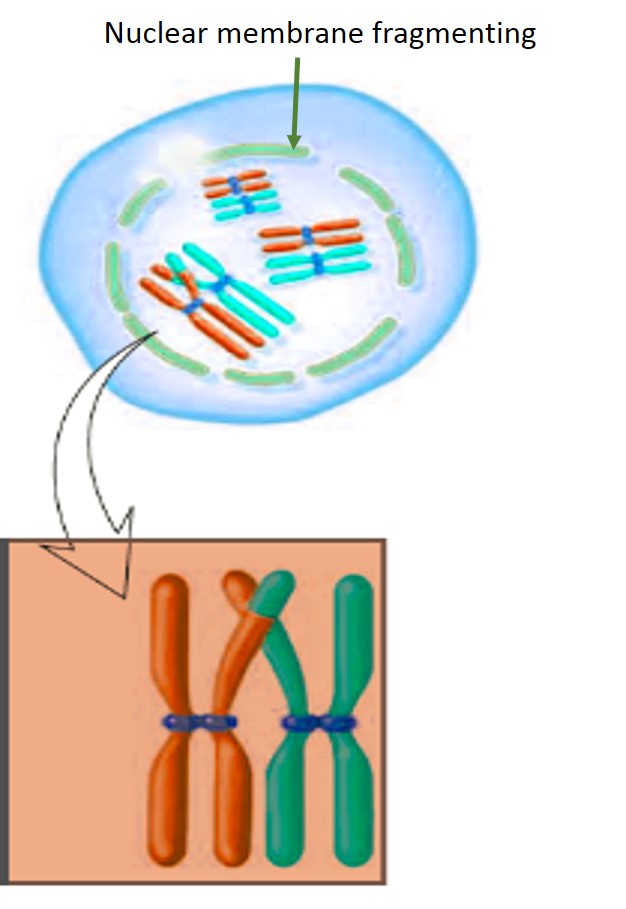
Diakinesis
- Terminalisation is completed.
- The non-sister chromatids remain in contact with each other at the telomeres.
- Complete disappearance of nuclear membrane and nucleoli.
Advertisements

