Cyclotron
Description:
Cyclotron is a device to obtain charged particles that have high velocity and high energy, such particles are required for experiments in nuclear physics.
To increase the velocity of charge particle, it need to be pass through a strong electric field again and again. In cyclotron magnetic field is used to turn the charge particle and let it enter back in the same magnetic field again.
Principle
Cyclotron work on two principles:
Electric field (E →) accelerates a charged particle i.e. increase its velocity.
Magnetic field (B →) turns its direction of motion to help charge re-enter the electric field.
Description
Components
- 2 DEES (hollow metal pots) with gap between them.
- Oscillator of 104 Volt with 106Hz oscillating potential difference.
- Electro-magnets to create magnetic field normal to cyclotron.
- Source of ion.
- Evacuated cover to eliminate air.
- Target.
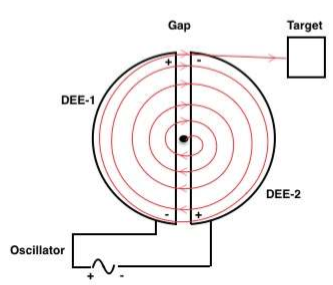
Assembly
Two hollow metal DEES are placed facing each other with a small gap between them, these DEES are connected with an oscillator that produces a potential difference between the DEES. As it is an oscillating supply the polarity changes after each half cycle. This arrangement of DEES and oscillator are placed between electro-magnets and the whole system is placed within an evacuated cover so that no air can enter in the device.
Working
Charge generated at source S is accelerated due to E→ in the gap increasing its velocity, with this increased velocity it enters DEE-2, inside DEE-2 there is no E→ hence B→ is prominent. This B→ turn it back to the gap. By this time polarity of E→ at gap is reversed by oscillator and it become along V→. So velocity increases further when it enters DEE1. This continues and velocity of the charge keeps on increasing, with this radius also increase due to relation.
Therefore, it makes a spiral shape. when radius is equal to radius of DEE then it is maximum, the kinetic energy and velocity is also maximum.
It is now allowed to move out and hit the target.
Relations
Centripetal force is given by –
We can derive multiple relations from the above equation.
Velocity of charge
Observation: Velocity depends on magnetic field, stronger is the magnetic field more will the number of rotations and final velocity will keep on increasing.
Radius of circular path
Angular velocity
Time period of rotation
Observation: The time period for the first and last rotation will be same.
Frequency / Cyclotron frequency
Kinetic energy of the rotating charge
Limitations
Cyclotron cannot work on neutrons, as the charge on neutrons is zero, so effect of electric and magnetic field on neutrons is zero.
According to Einstein’s equation -
At high velocity the mass increases, so time period of rotation will also increase, Hence the synchronization between velocity and electric field will be disturbed and they go out of step and there is no further acceleration of charge.
Therefore, we cannot increase the velocity beyond this velocity.

