Magnetic Field on The Axis of A Current Carrying Circular Coil
Description:
Consider a circular conducting coil of radius ‘a’ carrying current i. The loop lies on yz plane and its axis lies on x axis. Let us derive field at point P at a distance x from the center. Consider a small element at dl on the coil.
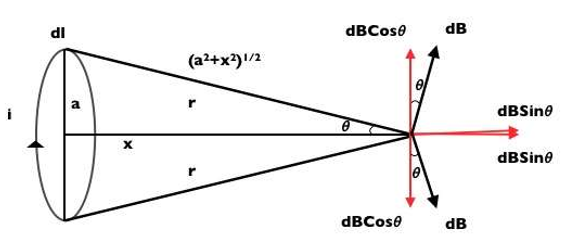
As the loop lies perpendicular to the plane of paper and vector r→ in the plane of paper.
Hence angle φ between dl→ and r→ is 90o
Magnetic field dB→ can be resolved into two components one dBsinθ parallel to the axis of the loop and other dBcosθ perpendicular to the axis.
From the symmetry of the system it can be seen that diametrically opposite elements contribute to cancel the perpendicular components whereas parallel components are added up.
B = ∫ dBsinθ
Thus,
From the diagram we can observe:
r = √(a2 + x2 and sinθ = a√(a2 + x2
As we know area of circular coil is
A = πa2
For coil with N turns -
We have Magnetic dipole moment of coil
𝑀 = 𝑁𝑖𝐴

