Magnetic Dipole Moment of Revolving Electron Gyromagnetic Ratio
Description:
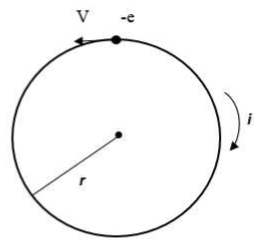
When an electron moves in a circular path there is a generation of electric current, this electric current is given by -
i = -e/T
The negative sign indicates that the direction of current is opposite to the motion of electron i.e. if the electron is revolving in anti-clockwise direction the current will have a clockwise direction.
Time period of revolution -
T = 2πr/V
Frequency of revolution -
υ = V/2πr
Angular velocity of revolution -
ω = V/r
Current can be expressed in various forms such as,
i = eV/2πr
i = ev
i = eω/2π
As revolving electron is generating current there will be a generation of magnetic field and it acts similar to magnetic field generated by current carrying circular coil.
Magnetic dipole moment of a current carrying circular coil is -
μ = NIA
For a single cycle N=1,
∴ μ = IA
Multiply and divide by m (m = mass of electron)
As we know angular momentum is 𝐿 = 𝑚𝑉𝑟
Gyromagnetic ratio
Ratio between magnetic dipole moment μ and Angular Momentum L is a constant known as gyromagnetic ratio and it is given by -
μ/L = e/2m
Observation
Whenever angular momentum of an electron increases its magnetic dipole moment also increases.
μ/L = 8.8 × 10-10 C Kg-1

