Electric Dipole - Electric Field on Axial Line
Description:
To calculate electric field created by a dipole on the axial line ( on the same line joining the two charges),
All the measurement of distances are to be taken from the centre(O).
Let the distance between O to +q and O to –q be ‘l’. So, total length between +q and –q will be ‘2l’.
Take a point ‘p’ on the axial line at the distance ‘r’ from the centre as shown in figure.
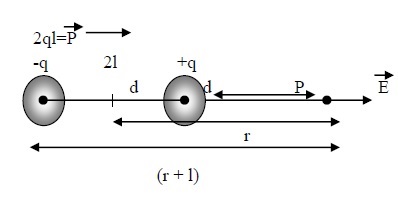
Now, we wish to calculate electric field at point ‘P’.
By using the formula for electric field due to point charge,
Electric field due to +q = +14πε0 q(r - l)2
The distance between (P and +q) = (r-l)
Electric field due to -q = -14πε0 q(r + l)2
The distance between (P and -q) = (r + l)
(Electric field due to +q will be positive and electric field due to- q will be negative)
Since electric field is a vector quantity so, the net electric field will be the vector addition of the two.
So, the net electric field E = E1 + E2
E = 14πε0 q(r - l)2 - 14πε0 q(r + l)2
E = q4πε0 [1(r - l)2 - 1(r + l)2]
On solving the equation we get −
E = q4πε0[(r + l)2 - (r - l)2(r - l)2(r + l)2]
E = q4πε0 4rl(r2 - l2)2 ......(1)
We know that the dipole moment or effectiveness of dipole (P) is given by −
P = 2ql
Therefore, putting this value in eq(1), we get
E = 14πε0 2Pr(r2 - l2)2 ......(2)
Certain assumptions are made based on this equation −
Since, the dipole is very small so ‘l’ is also very small as compared to the distance ‘r’.
So, on neglecting ‘r’ with respect to ‘l’ we get −
E = 14πε0 2Prr4 (from eq(2))
⇒ E = 14πε0 2Pr2
E = 14πε0 2Pr2
Note − Electric field on the axial line of dipole is not 0. Its magnitude is resultant as expressed above.
Direction of electric field in Axial line
The direction of the electric field due to point charge +q at point P will be away from itself whereas, The direction of the electric field due to point charge -q at point P will be towards itself.
Since the electric field due to charge +q is always larger than –q (as the distance of point P from +q is smaller than –q), So the resultant direction of electric field will be away from charge +q (i.e towards right).
The direction of electric field on the axial line is always same as the direction of dipole moment.

