Electric Dipole - Torque on Dipole kept in Electric Filed
Description:
A dipole is kept in a uniform external electric field which is created by some arrangements. The electric field intensity is same everywhere in the field. Figure is shown below −
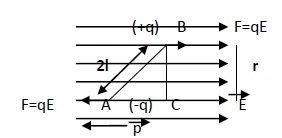
- E→ represents the direction of electric field
- P→ represents the direction of dipole moment
- Θ represents the angle between E→ and P→
We need to calculate the net force and torque on the dipole −
Calculating net force on dipole
Force due to positive charge (+q) = qE (force act in the direction of E)
Force due to positive charge (-q) = -qE (force act opposite to the direction of E)
Net force = zero
Note
Since, the magnitude of force due to both the charges are equal but the direction is opposite so the net force on the dipole is zero.
As the net force on the dipole is zero so dipole will not have linear motion. ( for a body to carry linear motion, net force cannot be equal to zero)
TORQUE
Whenever there is a couple of force OR Torque acting on a body, the body rotates. The figure shows that the two equal and opposite forces are acting of the same body but at a different points and these points are separated by a fixed distance. So these all satisfies the necessary condition for the body experiencing torque.
Therefore, torque (τ)= Force * distance between forces i.e (BC)
From fig: BC2l = sinθ therefore BC = 2l sinθ
(τ) = qE 2l sinθ
We know (2ql= dipole moment P)
(τ) = PE sinθ
Here, P ≠ 0, E ≠ 0, Sinθ ≠ 0, we conclude that the dipole experiences a torque.
In vector form it is τ→ = P→ × E→

