Electric Field Distribution of Charge in Full Sheet
Description:
Sheet Charge −
Charge distributed all over a surface is called sheet of charges.
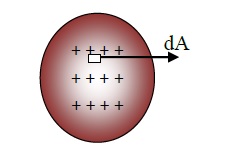
Introducing Arial charge density ‘σ’(sigma)
The charge per unit area is called Arial charge density and it is denoted by ‘σ’(sigma).
σ = Q/A (Coulomb m-2)
to find the electric field at a distance ‘r’ from the sheet of charge.
Calculating electric field due to ‘sheet of charge’ at distance ‘r’
An infinitely small area (dA) of the sheet is taken as shown in the figure (1)above.
Since, dA is very small so the charge on it would be same as that in a point charge.
if area 1m2 has the charge = σ
Then, area dA will have the charge = σdA.
So, dE = 14πε0σ dAr2r̂ .........(1)
Here, dE is the very small part of electric field due to dA.
So, electric field (E) due to the full sheet (A) can be calculated by integrating eq (1) both sides within the limit (0-A)
So ∫ dE = 14πε0A∫0σr2dA
⇒ E = 14πε0A∫0σr2dA
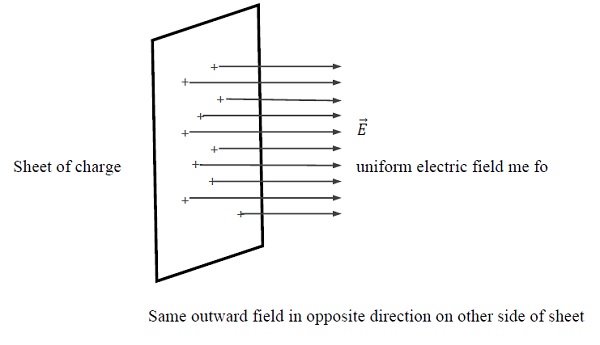
- Resultant shape of electric field at every point of the sheet is
Charges Distributed Over The Volume
Whenever charges are distributed all over the volume of a non conductor, the charges not only accumulate at the surface of but also remains within the non conductor.
Introducing volumetric charge density ρ, (rho) to find the electric field at a distance ‘r’ from the non conducting sphere containing charges.
volumetric charge density (ρ) −
The total charge per unit volume is called volumetric charge density and it is denoted by ‘ρ’(rho). ρ = Q/V unit : coulomb m-3
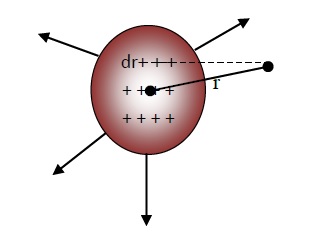
An infinitely small volume (dV) of the sphere is taken as shown in the figure above.
Calculating electric field due to ‘volumetric charge’ at distance ‘r’
Since, dV is very small so the charge on it would be same as that in a point charge.
if area 1m3 has the charge = ρ
Then, volume dV will have the charge = ρdV.
So, dE = 14πε0ρdVr2 r̂ ........(1)
Here, dE is the very small part of electric field due to dV.
So, electric field (E) due to the full sphere (V) can be calculated by integrating eq (1) both sides within the limit (0-V)
So ∫ dE = 14πε0 v∫0 ρ.dvr2
Electric field (E) due to the full sheet (A) of charge = 14πε0ρr2V
The resultant shape of electric field due to charges of nonconductor is Normal to the surface of nonconductor as shown in figure −
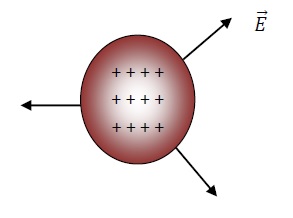
Electric field at a distance are different for different distribution of charges.

