Electric Field due to Pair of Sheets with Charge
Description:
To study electric field due to infinitely large plane sheets of charges if they are placed together where the charges and charge density on the two sheets may be similar or opposite we. will find result for both the cases.
For the study we consider three region in the space as shown in figure −
- within the plates
- outside the left
- outside the right.
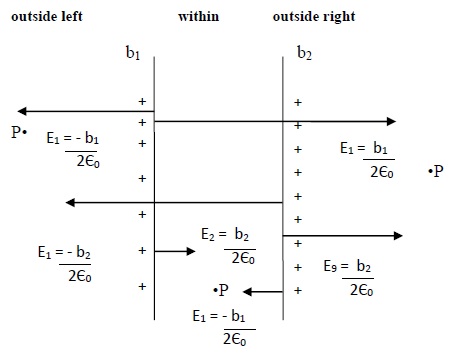
Electric field due to plates with similar charge
Region outside left
We know,
For a single sheet of charges E = σ/ 2ε0
If we take a point normally outside the sheet(1) in left region, the electric field at that point due to sheet(1) will be
E1 = -σ1/ 2ε0 (negative sign is due to the direction of electric field towards left).
Now, the electric field at the same point due to sheet(2) will be
E2 = -σ2/ 2ε0
Here, the electric field is normally out of the surface in left direction as shown in figure.
So electric Field for outside left Eleft = E1 + E2 = -12ε0(σ1 + σ2)
Special Case
If both the plates have equal charge density i.e (σ1 = σ2 = σ) then total electric field at outside left region will be −
Eleft = E1 + E2 = -σ/ ε0 (negative shows direction of resultant E towards right)
Region within the plates
If we take a point in between the two sheets(1) then, the electric field at that point due to sheet(1) will be −
E1 = σ1/ 2ε0 (positive sign is due to the direction of electric field is towards right)
Now, the electric field at the same point due to sheet(2) will be
E2 = -σ2/ 2ε0 (negative sign is due to the direction of electric field towards left)
So electric field within the plates will be − Ewithin = E1 + E2 = -12ε0(σ1 - σ2)
Special Case
If both the plates have equal charge density i.e (σ1 = σ2 = σ) then total electric field within the plates will be −
Ewithin = E1 + E2 = 0
Region outside right
If we take a point normally outside the sheet(2) in right region, the electric field at that point due to sheet(1) will be −
E1 = σ1/ 2ε0 (positive sign is due to the direction of electric field is towards right)
Now, the electric field at the same point due to sheet(2) will be
E2 = σ2/ 2ε0 (positive sign is due to the direction of electric field towards right)
So electric field outside right − Eright = E1 + E2 = 12ε0(σ1 + σ2)
Special Case
If both the plates have equal charge density i.e (σ1 = σ2 = σ) then total electric field at outside right region will be −
Eright = E1 + E2 = σ/ ε0 (positive shows direction of resultant ’E’ is towards right)
Note − If there are two charged plates placed parallel to each other with equal charge density, then, out side there will be some electric field and within the plates there will be NO electric field.
If a plate contain charge on both the side of it then it behave like two plates placing parallel to each other. In that case the electric field at any point will be same as in case of electric field at a point due to two charged plates.
Electric field due to plates with different charge.
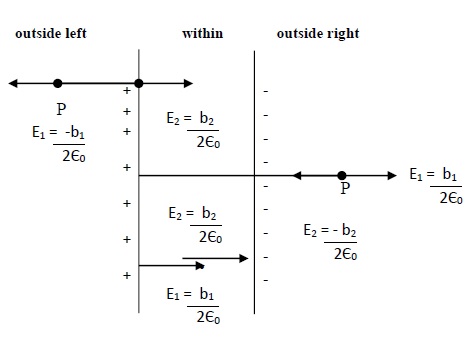
Region outside left
If we take a point normally outside the sheet(1) in left region, the electric field at that point due to sheet(1) will be
E1 = -σ1/ 2ε0 ( negative sign is due to the direction of electric field towards left).
Now, the electric field at the same point due to sheet(2) will be −
E2 = σ2/ 2ε0 (positive sign is due to the direction of electric field towards right).
The direction of electric field with respect to negative charge is always towards negative charge. O the direction is towards right. It is as shown in figure.
So electric Field for outside left Eleft = E1 + E2 = 12ε0(σ1 - σ2)
Special Case
If both the plates have equal charge density i.e (σ1 = σ2 = σ) then total electric field at outside left region will be −
Eright = E1 + E2 = 0 (positive shows direction of resultant ’E’ is towards right)
Region within the plates
If we take a point in between the two sheets(1) then, the electric field at that point due to sheet(1) will be −
E1 = σ1/ 2ε0 (positive sign is due to the direction of electric field is towards right)
Now, the electric field at the same point due to sheet(2) will be
E2 = σ2/ 2ε0 (positive sign is due to the direction of electric field towards right)
So electric field within the plates will be − Ewithin = E1 + E2 = 12ε0(σ1 + σ2)
Special Case
If both the plates have equal charge density i.e (σ1 = σ2 = σ) then total electric field within the plates will be −
Ewithin = E1 + E2 = σ/ ε0
Region outside right
If we take a point normally outside the sheet(2) in right region, the electric field at that point due to sheet(1) will be
E1 = σ1/ 2ε0 (positive sign is due to the direction of electric field is towards right)
Now, the electric field at the same point due to sheet(2) will be
E2 = -σ2/ 2ε0 (negative sign is due to the direction of electric field towards left)
So electric field outside right − Eright = E1 + E2 = 12ε0(σ1 - σ2)
Special Case
If both the plates have equal charge density i.e (σ1 = σ2 = σ) then total electric field at outside right region will be −
Eright = E1 + E2 = 0 (positive shows direction of resultant ’E’ is towards right)
Note − If there are two dissimilar charged plates placed parallel to each other with equal charge density, then, outside there will be NO electric field and within the plates there will be some electric field.

