Electron theory of Electrification
Description:
In an atom the net charge is Zero. In any atom there is a nucleus and electron revolves around it. When nucleus was separated from an atom it was found that the electrons carry negative charges. Since, an atom is neutral and electrons are negative so it was concluded that nucleus is positively charged.
Conclusion
1. Every atom consist of equal number of electrons in the orbit which have -ve charge and equal number of protons in the nucleus which have +ve charge. So its net charge is zero.
2. The net charge on one electron is the minimum charge on the particle. Charge on 1 electron is called as a fundamental charge / basic charge.
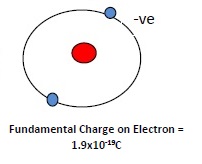
3. Net charge on an atom is zero due to equal +ve and -ve charges.Nucleus+ve.
4. The excess of electron make the particle negatively charged.
5. The deficiency of electron makes particle positively charged.
Note −
1. Electron is only responsible for electrification.
2. Because of its light weight it is only electron which moves and not nucleus / proton. Whenever we rub two bodies, then there is an exchange of electron between the two bodies due to friction. Due to which there is excess of electron in one body (making it negatively charged) and loss of electron in other( making it positively charged).
3. Proton is not mobile because
- It is in the nucleus.
- Because of its heavy mass (1837 times heavier than electron).

