Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - Nature of C-X bond
Description:
The C − X bond is polarised such that partial negative charge is developed on the electronegative halogen atom while partial positive charge is developed on carbon.
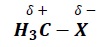
Electronegativity of X: F(3.98) > Cl(3.16) > Br(2.96) > I(2.66)
Electronegativity of C: 2.55
Since the difference in electronegativity is maximum in C − F, it is most polar.
Bond length (A0)
Increases in the order −
The size of X increases down the group, F < Cl < Br < I
C − F < C − Cl < C − Br < C − I
1.39 < 1.78 < 1.93 < 2.14
As the atomic size of carbon and fluorine are very similar, the orbitals overlap effectively leading to very strong bond. In C − I, however, due to very large atomic size of iodine and small size of carbon atom, the orbital interaction is weak resulting in weak bond strength. Stronger the bond, lower is the bond length, thus, C − F has lowest bond length of 1.39 A0.
Bond enthalpy order
C − F > C − Cl > C − Br > C − I
Stronger the bond, greater the amount of energy required to break that bond. Thus, C − F has highest bond enthalpy.
Dipole moment
The order of dipole moment is: CH3Cl > CH3F > CH3Br > CH3I
Dipole moment of alkyl halides are −
CH3F − 1.847D, CH3Cl − 1.860 D, CH3Br − 1.830 D, CH3I − 1.636 D
Dipole moment is a product of both charge and distance.
μ = q × d
Thus, although F > more electronegative > Cl, C − F bond is much shorter than C − Cl bond such that the value of dipole moment (q×d), will be lower for CH3F as compared to CH3Cl.
Bond Length: C − F (139 pm) while C − Cl (178 pm)

