Reactions of Haloarenes - Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
Description:
Chlorobenzene can be converted into phenol under drastic conditions (Temperature:623 K and Pressure:300 atm).
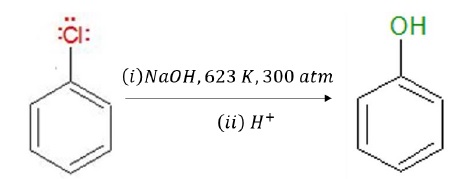
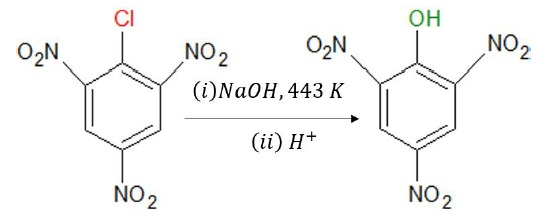
The presence of an electron-withdrawing group (−NO2) at ortho − and para−positions increases the reactivity towards NS reactions.
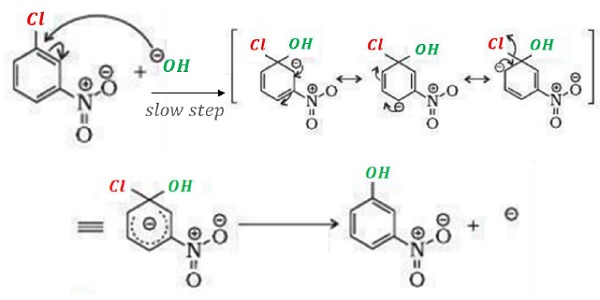
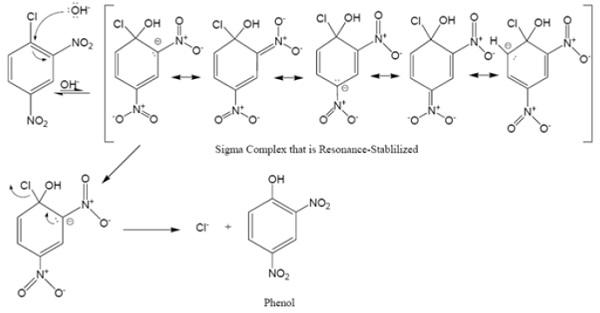
Mechanism of Aromatic Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction
Note: When electron-withdrawing groups are present at meta −postions, no effect is observed on reactivity. Why??
When electron-withdrawing groups are present at meta −postions, no effect is observed on reactivity.
During resonance, the negative charge is developed at ortho − and para − positions which are stabilized via resonance by −NO2 group.
Electron density is withdrawn by −NO2 group when it is present at ortho − and para − positions such that it facilitates the attack of incoming nucleophile.
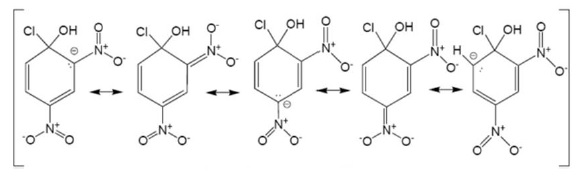
However, when −NO2 is present at meta position, no resonance structure has negative charge on carbon bearing −NO2 group as electron density is at ortho and para positions.
Thus, no effect on reactivity towards nucleophilic substitution reaction is observed when −NO2 is present at meta position.