Problem on SN1 & SN2
Description:
Problem
Which of the following compounds will undergo SN2 reaction faster?
1. 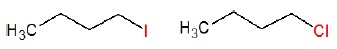
2. C6H5CH2Br, C6H5CH(C6H5)Br, C6H5CH(CH3)Br, C6H5C(CH3)(C6H5)Br
Solution
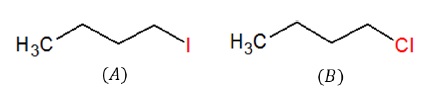
Both are 10 alkyl halides.
Reactivity towards SN2 now depends on the ease with which the X− ions leave.
Leaving group: I− > Br− > Cl− > F−
Since I− is a better leaving group than Cl−, (A) is more reactive than (B) towards SN2 reaction.
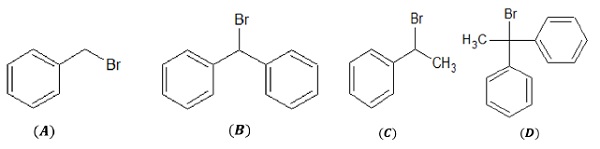
2.
Reactivity of alkyl halides towards SN2: 10 > 20 > 30
Both (B) and (C) are secondary halides while (A) is primary and (D) is tertiary halide.
Due to steric hindrance, (C) > more reactive > (B) as (B) is more sterically hindered due to the presence of two bulky phenyl rings.
Order of reactivity (SN2): (A) > (C) > (B) > (D)
In order to determine the reactivity of the above alkyl halides towards SN1 reaction, stability of the carbocation is considered. We know that reactivity of alkyl halides towards SN1 reaction is 30 > 20 > 10 as 30 carbocation is more stable than secondary and primary.
(A):10carbocation,(D):30carbocation. (B)and (C):20carbocation.
Among (B)and (C), (B) gives more stable carbocation due to resonance stabilization via two phenyl rings, resulting in greater dispersal of positive charge as compared to (C).
Thus, the order of reactivity of the given alkyl halides towards SN1:(D) > (B) > (C) > (A)
Order of reactivity (SN2): (A) > (C) > (B) > (D)
Order of reactivity (SN1):(D) > (B) > (C) > (A)

