Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions (II) Problem 7
Description:
Problem
Arrange the following in their reactivity towards SN2 reaction.
1. 2 − Bromo − 2 − methylbutane, 1 − bromopentane, 2 − bromopentane.
2. 1 − Bromobutane, 1 − Bromo − 2,2 − dimethylpropane, 1 − Bromo − 2 − methylbutane, 1 − Bromo − 3 − methylbutane.
Solution
SN2 reaction is a one-step process which involves the formation of a transition state.
Since transition state is highly unstable due to carbon bearing 5 bonds, steric hindrance needs to be minimized.
Thus, the order of reactivity of alkyl halides towards SN2 reaction is 10 > 20 > 30
Set 1 − 2 − Bromo − 2 − methylbutane, 1 − Bromopentane, 2 − Bromopentane.
The reactivity of the alkyl halides towards 𝑆𝑁2 reaction will follow the order: 10 > 20 > 30
1 − Bromopentane > 2 − Bromopentane > 2 − Bromo − 2 − methylbutane
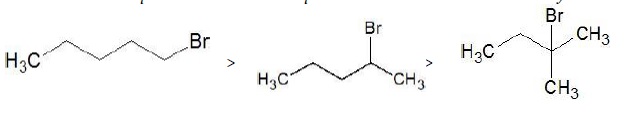
Set 2 − 1 − Bromobutane, 1 − Bromo − 2,2 − dimethylpropane, 1 − Bromo − 2 − methylbutane, 1 − Bromo − 3 − methylbutane
| Substrate | Structure | Type |
|---|---|---|
| 1 − Bromobutane (I) | 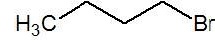 | 10 Primary |
| 1 − Bromo − 2,2 − dimethylpropane (II) | 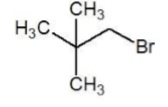 | 10 Primary |
| 1 − Bromo − 2 − methylbutane (III) | 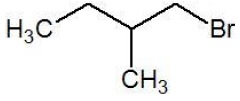 | 10 Primary |
| 1 − Bromo − 3 − methylbutane (IV) | 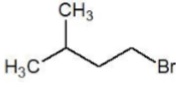 | 10 Primary |
Since all the alkyl halides given are primary, reactivity towards SN2 reaction will be determined based on steric inhibition.
Steric hindrance is determined by crowding around carbon bearing halogen atom.
Thus, the order of reactivity towards SN2 reaction is −
(I) > (IV) > (III) > (II)

