Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - Nomenclature
Description:
In order to write the IUPAC name of a given organic compound, we need to identify −
- Parent chain (longest hydrocarbon).
- Principal functional group (suffix)
- Substituents and its position(s) (prefix).
CH3 − CH2 − CH(Cl) − CH3
Common Name: sec − Butylchloride;
IUPAC Name − 2 − Chlorobutane
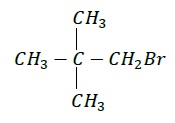
Common Name: neo − Pentylbromide
IUPAC Name − 1 − Bromo − 2,2 − dimethylpropane
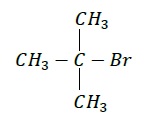
Common Name: tert − Butylbromide
IUPAC Name − 2 − Bromo − 2 − methylpropane
CH2 = CH − Cl
Common Name: Vinyl Chloride
IUPAC Name − Chloroethene
CH2 = CH - CH2Br
Common Name: Allyl Bromide
IUPAC Name − 3 - Bromoprop - 1 - ene
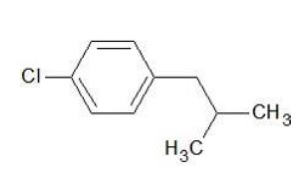
IUPAC Name − 1 - Chloro - 4- (2 - methylpropyl)benzene
Dihaloalkanes having the same type of halogen atoms are called alkylidene or alkylene dihalides.
When dihalo compounds having same type of halogen atoms are present on the same carbon atom − geminal dihalides.
When dihalo compounds having same type of halogen atoms are present on the adjacent carbon atoms − vicinal dihalides.
| CH3 - CHCl2 | Ethylidene chloride | gem-dihalide | 1,1 − Dichloroethane |
| CH2Cl - CH2Cl | Ethylene dichloride | vic-dihalide | 1,2 - Dichloroethane |

