Reactions of Haloarenes - Electrophilic Substitution Reactions
Description:
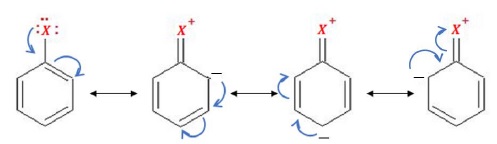
Since haloarenes are electron-rich, these undergo electrophilic substitution reaction where the attacking species is an electrophile. Due to +M effect, electron density is concentrated at ortho −and para −positions.
The reaction of haloarenes towards electrophilic substitution reactions is slow as compared to benzene because although ortho/para directing, X(halogens) are deactivating due to the –I effect and withdraws electrons from the benzene ring.
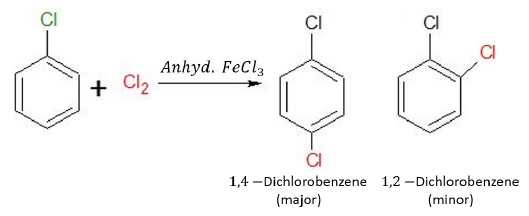
Halogenation
Halogenation of chlorobenzene in the presence of lewis acids gives ortho and para substituted dihalobenzenes. The electrophile in this reaction is Cl+.
Nitration
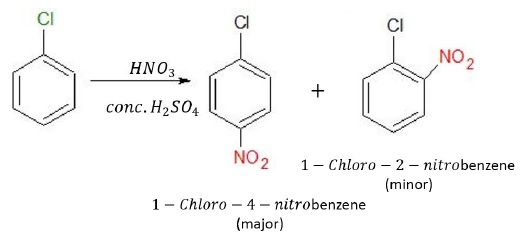
Nitration of halobenzenes in the presence of conc.H2SO4 and HNO3 give ortho and para substituted products. The electrophile in this reaction is NO2+.
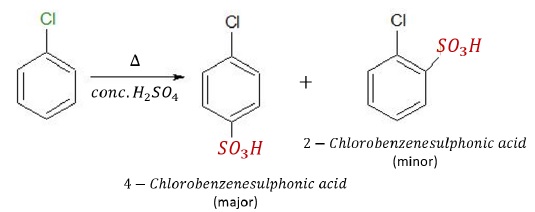
Sulphonation
Sulphonation of chlorobenzene in the presence of conc.H2SO4 and heating gives para − and ortho − Chlorobenzenesulphonic acids.
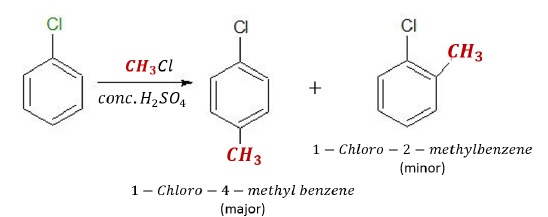
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation Reactions − give the following products.
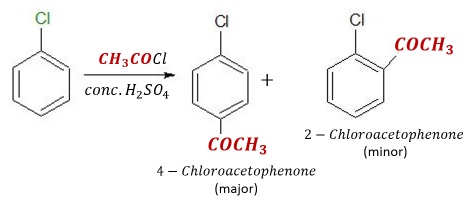
Friedel-Crafts Acylation Reactions