Electronic Displacement Effects - Hyperconjugation Alkenes
Description:
Delocalisation of electrons by hyperconjugation in alkenes can be shown as given below.
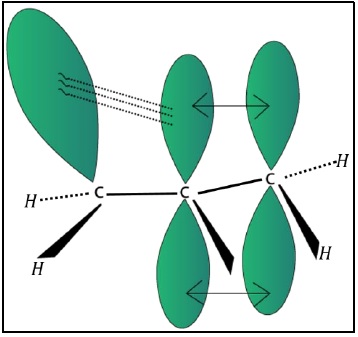
The hyperconjugative effect can also be considered by regarding C − H bond as possessing partial ionic character due to resonance.
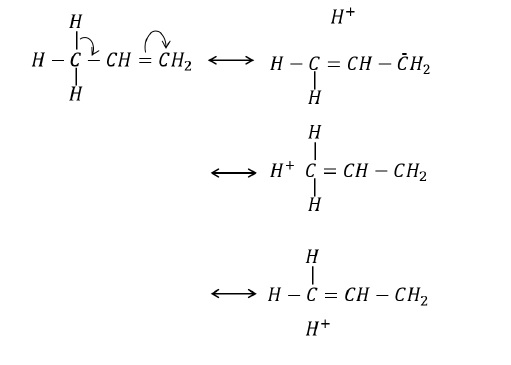
Example 1 − Which among the given alkenes has maximum stability?
CH3 − CH = CH2, CH3 − CH2 − CH = CH2 and (CH3)2 − CH − CH = CH2
Solution − Greater the number of α − hydrogen, greater is the stability via hyperconjugation.
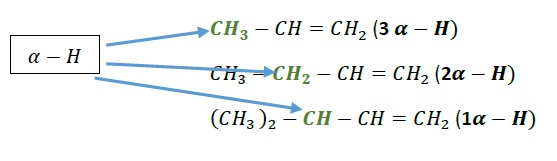
Example 2 − Write the order of decreasing stability for the given substituted benzenes.
C6H5 − CH3,C6H5 − CH2CH3,C6H5 − CH − (CH3)2,C6H5 − C(CH3)3
Solution −
The decreasing order of electron density on phenyl ring is as follows −
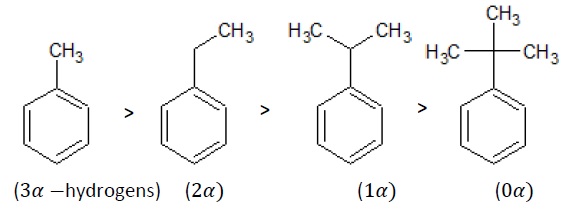
More the number of α-hydrogens, greater is the stability of that molecule.
Note − When multiple electron displacement/stabilizing effects are involved in a given molecule, the order of preference is: Resonance > Hyperconjugation > Inductive Effect.

