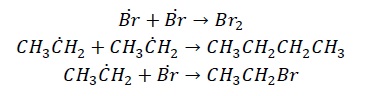Organic Reactions - Free Radical
Description:
Involve the addition of a radical across an organic molecule.
For example, addition of a halogen across a double bond follows free-radical mechanism.
Due to their high reactivity, these are non-selective in nature.
There are 3 stages of free radical reaction. Let’s take an example of free radical halogenation of ethane.
Initiation − Halogens in the presence of heat or UV-radiation undergoes homolytic fission giving free radicals.
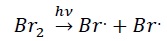
Propagation − The bromine radical attacks ethane by breaking the C - H bonds and generates ethyl free radical. The ethyl radical further attacks another bromine molecule regenerating the bromine radical.
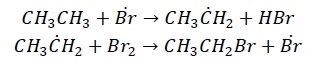
The reaction is non-selective and results in parallel propagation steps such as −
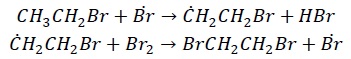
Termination − The reaction terminates when the reactant molecules are completely consumed or due to the following side reactions.