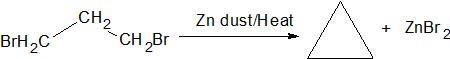Organic Reactions - Elimination
Description:
Two atoms or groups are removed from the molecule to form the product.
It is the opposite of addition reaction and the product contains multiple bonds (results in unsaturation).
There is release/elimination of small molecules etc.
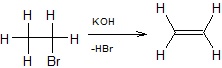
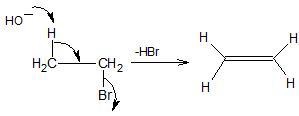
The above reaction is called dehydrohalogenation, where hydrogen halide (HBr) is eliminated.
Depending on the relative positions of the atoms or groups eliminated, the elimination reactions are classified as α, β or γ elimination reactions.
α - elimination − Two atoms or groups are eliminated from the same atom such that electron deficient reactive intermediate is formed, which further reacts to form final stable products.
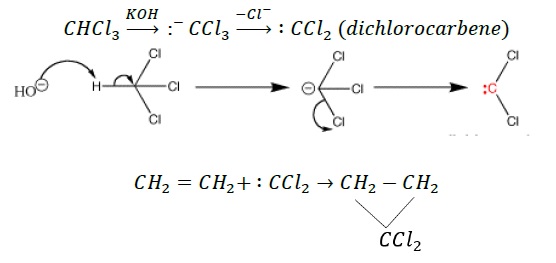
β - elimination − Two groups are removed from adjacent carbon atoms (α,β) resulting in the formation of a π −bond.
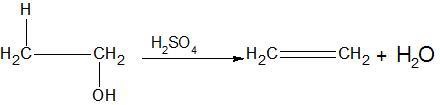
Dehydrohalogenation is also an example of β − elimination.
γ - elimination − The two groups are eliminated from α and γ positions resulting in the formation of a three membered ring.