Isomerism - Stereoisomerism
Description:
Stereoisomers are those compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the relative positions or arrangement of atoms or groups in space.
It can be broadly classified into conformations and configurations.
Conformations are orientations obtained by free rotation around C − C sigma bonds.
The two types of stereoisomers, geometrical and optical isomers are called configurations which are rigid or fixed molecules and cannot be interconverted by rotation around C − C bonds.
It arises when due to the presence of a double bond (or a ring), free rotation between carbon atom is restricted.
In that case, the two groups attached to the carbon atom are different, such that it results in two different relative arrangements of atoms or groups in space called configurations.
Since they differ in their relative arrangement of groups in space, these are called stereoisomers and these type of stereoisomers is called geometrical isomers.
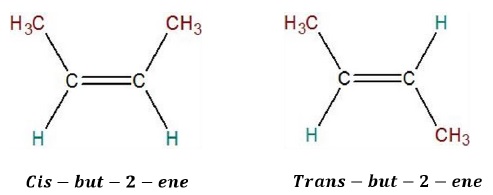
Also called configurational isomerism or cis − trans isomerism.
Two types of geometrical isomers: Cis and Trans.
Example: But − 2 − ene (CH3CH = CHCH3)
Optical isomers are stereoisomers which differ in their behavior towards plane polarized light.
More about optical isomers will be dealt in the later chapters.

