Isomerism - Problem 3
Description:
Problem − Briefly reason why alkenes and cycloalkanes exhibit cis − trans isomerism?
Solution − Cis − trans isomerism is exhibited due to restricted/hindered rotation of bonds.
The presence of double bond: free rotation around C = C is not possible as it results in the breaking of the π − bonds formed by the parallel overlap of p −orbitals. Thus, due to restricted rotation, the two isomers, cis & trans cannot interconvert, resulting in geometrical isomerism.
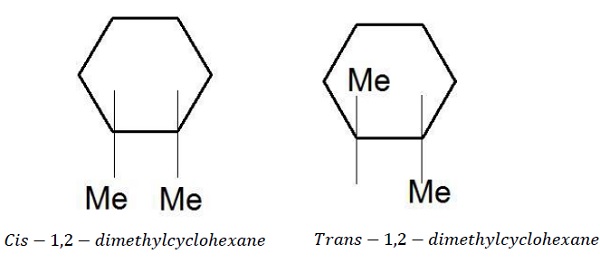
Cycloalkanes due to rigid structure, rotation around C − C bond is restricted thus resulting in distinct arrangement of atoms in space. Like alkenes, cycloalkanes are capable of cistrans isomerism. When two substituents on a ring point to the same face, they are cis. When the two substituents point to opposite faces, they are trans. Although both have same connectivities of atoms, due to their difference in the spatial arrangement of atoms, these exhibit geometrical isomerism.