Purification Techniques - Differential Extraction
Description:
The partial removal of a substance from a solution or mixture by dissolving it in another, immiscible solvent in which it is more soluble.
When an organic compound is present in an aqueous medium, it is separated by shaking it with an organic solvent, in which it is more soluble than water.
The organic and aqueous layer are immiscible.
The compound is retrieved by distillation or evaporation of organic solvent.
It is carried out in a separating funnel.
Commonly employed solvents are ether, benzene and chloroform.
Process of differential extraction involves the following steps −
Aqueous solution containing organic compound is mixed with small amount of organic solvent in a separating funnel.
The funnel is shaken and the mixture is allowed to settle.
Two distinct layers are formed. Most organic layers are less dense than water and floats on top of the aqueous layer.
The lower aqueous layer is removed and solvent layer is collected separately.
The solute is finally recovered from the organic solvent by distillation.
Note: organic solvent should have low boiling point.
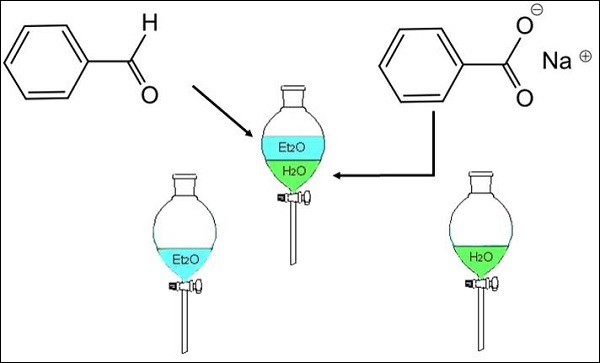
Example: separation of a mixture of benzaldehyde and sodium benzoate can be done by adding the mixture to a water-ether liquid mixture. Benzaldehyde dissolves in ether while sodium benzoate being polar dissolves in the aqueous layer. The two layers are formed after shaking the separating funnel and the fractions are separated.
Benzaldehyde is obtained by distillation.