Quantitative Analysis - Carbon & Hydrogen
Description:
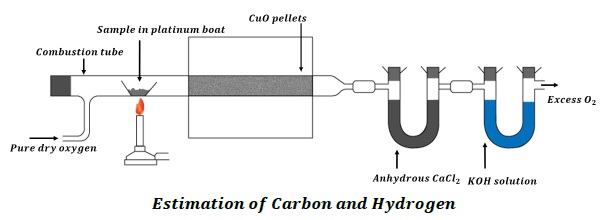
A known mass of an organic compound is burnt in the presence of excess of oxygen and copper (II) oxide. Carbon and hydrogen are oxidized to CO2 and H2O respectively.
CxHy + (x +
y
4
)O2 → xCO2 + (
y
2
)H2O
The mass of water produced is determined by passing the mixture through a U −tube containing anhydrous CaCl2.
CO2 is absorbed in another U −tube containing concentrated solution of KOH.
The increase in the masses of CaCl2 and KOH gives the amount of water and CO2 from which the amount of carbon and hydrogen can be estimated.
For example,
Let the mass of organic compound be ′m′ g, mass of water and CO2 formed be m1& m2 (indicated by increase in the mass of U −tube).
Percentage of Carbon −
44 g of CO2 contains = 12 g carbon
m2 g contains =
m2 x 12
44
g
Now,
12 x m2
44
g of carbon is present in m g of organic compound.
Thus, percentage of carbon in the organic compound =
(12 x m2)
44 x m
x 100
Percentage of carbon =
12 x m2 x 100
44 x m
Percentage of hydrogen
18 g H2O contains = 2g
m1g of H2O contains hydrogen =
2 x m1
18
g
Now,
2m1
18
g hydrogen is present in m g of organic compound.
Thus, percentage of hydrogen in the organic compound =
2m1 x 100
18 x m
Percentage of hydrogen =
2 x m1 x 100
18 x m