Electronic Displacement Effects - What is Resonance?
Description:
Resonance theory states that when a molecule or ion can be represented by two or more Lewis structures, that differ only in the position of electrons, the actual molecule is represented by hybrid of resonance structures.
Examples are: Benzene and carbonate ion (CO32−)
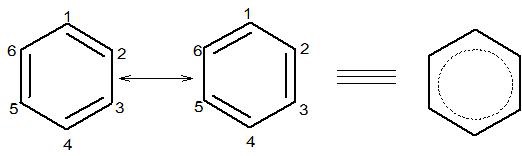
The two resonance structures contribute equally to the resonance hybrid.
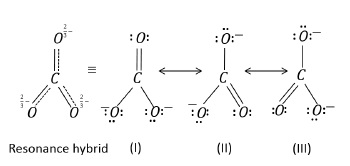
Structures (I), (II), (III) are the resonance or canonical structures that contribute to the actual resonance hybrid molecule.
Resonance (or canonical) structures are hypothetical.
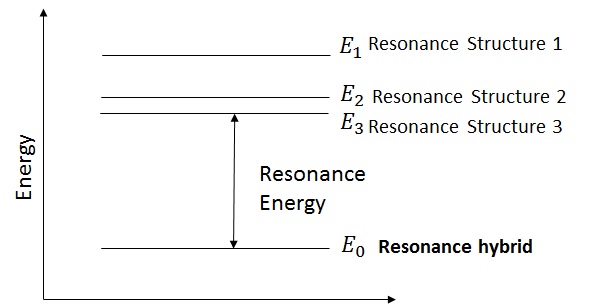
The energy of actual structure (resonance hybrid) is lower than any of the resonance structures.
Greater the stability of resonance contributor, more it contributes towards the resonance hybrid.
More the number of resonance structures, greater is the resonance energy.
Resonance energy − is the energy difference between actual structure and lowest energy resonance structure.
Order of energy of resonance structures are: 1 > 2 > 3. Resonance structure 3 has the lowest energy, thus it is most stable and contributes maximum towards the resonance hybrid.
Resonance Energy = E3 − E0
Rules of writing resonance structures: The resonance structures have −
Same positions of nuclei.
Same number of unpaired electrons.
All of the structures must be proper Lewis structures.
The most stable resonance structure is the one having −
Most number of covalent bonds.
All the atoms with octet configuration.
Least separation of opposite charge.
Negative charge residing on electronegative atom and positive charge on electropositive atom.
Note that equivalent resonance structures make equal contributions to the hybrid. Such a system is highly stable.
Example: allyl carbocation
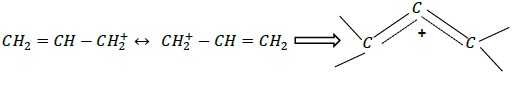
Rules of writing resonance structures −
Example − Which of the following resonance structures is the most stable?
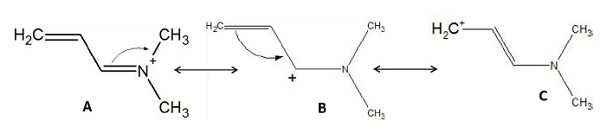
Solution − Structure A is the most stable as
- All atoms have completely filled octets.
- It has maximum number of covalent bonds.
While Structure B and C have fewer covalent bonds and incomplete octets.

