Electronic Displacement Effects - Inductive Effect
Description:
Occurs in a covalent bond formed between atoms of different electronegativity.
Electron cloud is drawn towards more electronegative atom.
Partial charges are developed on both the atoms.
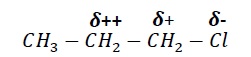
The polarization of σ bond results in Cl having δ − and adjacent carbon having δ + charge. This polarization of σ bond caused by polarization of adjacent σ −bond is called inductive effect.
The effect decreases with increase in distance from the electronegative substituent.
Related to the ability of substituents to withdraw or donate electron density to attached carbon atom with respect to hydrogen.
Electron-withdrawing groups: −X,−NO2,−COOH,−COOR,−OAr,(CH3)3N+ (−I effect).
Electron-donating group –R (alkyl) (+I effect).
Example: What would be the correct order of acidity of the given carboxylic acids?
Cl3CCOOH,ClCH2COOH,Cl2CHCOOH
The correct order of acidity of carboxylic acids is: Cl3CCOOH > Cl2CHCOOH > ClCH2COOH.
In acids, the electron-releasing inductive effect of the alkyl group increases the electron density on oxygen and thus hinders the breaking of the O-H bond, which consequently reduces the ionization.
Since Cl is an electronegative group, it withdraws electrons from the adjacent carbon via inductive effect.
This consequently pulls the electrons from –COOH group resulting in increased acidity.
Thus, greater the number of chlorine atoms, stronger is the inductive effect and more is the acidity of the carboxylic acids.
What will be the order of acidity in: CH3COOH,ClCH2COOH,HCOOH?
Solution −
Order of Acidity: ClCH2COOH (−I effect) > HCOOH > CH3COOH(+I effect).
pkα values: 2.82 (ClCH2COOH) < 3.74(HCOOH) < 4.86 (CH3COOH)

