Heterolytic Cleavage - Carbocations
Description:
Organic reactions proceeding via heterolytic cleavage is called ‘ionic’ or ‘polar’ reactions.
Bond is broken such that shared pair of electrons is retained by one of the fragments. A positive and
negatively charged species are formed.

Carbocation
Species having carbon atom with positive charge is called carbocation (or carbonium ion).
It is electron deficient as there are only 6 e− in its valence shell.
CH3+ ion is called methyl cation.
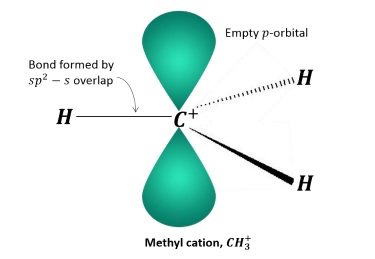
It has vacant 2pz orbital giving sp2 hybridization and has trigonal planar structure.
Carbocations can be
- primary (10) : CH3CH2+
- secondary (20): (CH3)2CH+
- tertiary (30): (CH3)3C+
Stability is determined by −
Hyperconjugation effects −
In carbocations, the conjugation is between σ bond of C − H and the positive charge on carbon.
CH3CH2+ (3α) < (CH3)2CH+ (6α) < (CH3)3C+ (9α)
More the number of α −hydrogens, more will be the stability of carbocation.
Inductive effects −
Since carbocation is electron-deficient, electron donating groups (EDGs) will stabilize it.
More the no. of alkyl groups (EDGs), greater is the stability.
Thus, order of stability of carbocations: 30 > 20 > 10
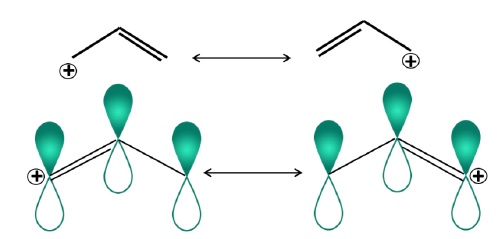
Resonance effects −
Adjacent π −bond stabilizes a carbocation. Carbocation has planar structure and empty p −orbital can overlap parallel with the adjacent π −bond resulting in delocalization of positive charge.
Adjacent Lone pair of electrons −
Atoms with lone pair of electrons adjacent to carbocation stabilizes the electron deficient species by donation of electrons.
Electron-withdrawing species such as nitrogen, oxygen, halogens also stabilize carbocations by donation of electrons forming π −bonds, which is a stabilizing influence.
For example,
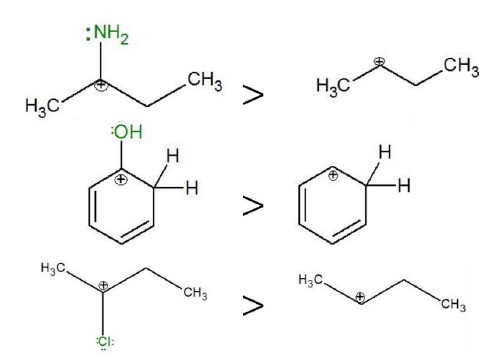
𝐶𝑙 exhibits −
- −I effect: destabilizes carbocation.
- +M/+R effect: stabilizes carbocation.
However, the priority of electronic effects −
Resonance > Hyperconjugation > Inductive effect
Thus, although Cl exhibits –I effect due to its electron-withdrawing inductive effect, priority is given to its stabilization of carbocations via resonance (+R) effect.

