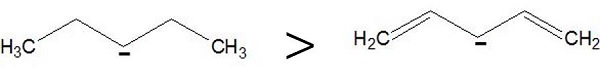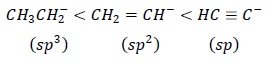Heterolytic Cleavage - Carbanion
Description:
Heterolytic cleavage resulting in carbon with negative charge is called carbanion.
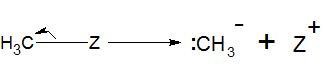
It has sp3 hybridization and tetrahedral structure.
Although it has 8 e− in its valence shell, it is a highly reactive species as the atomic size of carbon is small and negative charge leads to instability.
Stability is determined by −
Inductive Effect − Since, carbanions are electron rich, electron donating alkyl groups will increase the electron density making it unstable. It is thus stabilized inductively by electron withdrawing groups.
Thus, order of stability of carbanions −
10 (CH3CH2−) > 20(CH3)2CH− > 30(CH3)3C−
Electronegative atoms also stabilizes carbanions inductively by withdrawing the electrons from carbon atom which due to its small size cannot accommodate an extra electron and becomes highly reactive.
Resonance effect − A negative charge adjacent to π −bonds can disperse its charge through multiple atoms by resonance.
For example,
Hybridization − Hybridization with more s −character stabilizes carbanion. s −orbtial lies closer to the nucleus than p. Thus, sp > sp2 > sp3