Electronic Displacement Effects - Resonance Effect
Description:
It is defined as the polarity produced in molecule by interaction of two π-bonds (resonance effect) or a π bond and lone pair of electrons (mesomeric effect).
Alternate single and double bonds in open chain or cyclic compounds results in conjugation. In systems with conjugation, π-electrons are delocalised and polarity is developed.
Resonance effect can be of two types −
+R/+M effect − The transfer of electrons is away from the substituent group attached to the conjugated system.
Groups exhibiting +R/+M effect − −X,−OH,−OR,−OCOR,−NH2 − NHCOR
Example: Aniline
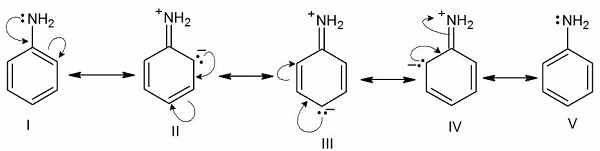
In +R effect, negative charge is developed at ortho and para positions.
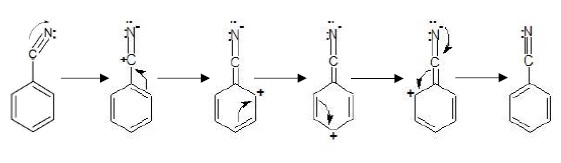
−R/−M effect − The transfer of electrons is towards the substituent group attached to the conjugated system.
Groups exhibiting −R/−M effect − −COOH,−CHO,Co,−CN,−NO2
Example: Benzonitrile
In –R effect, positive charge is developed at ortho and para postions.