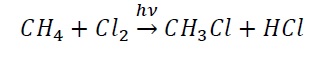Organic Reactions - Substitution
Description:
An atom or a group of atom is substituted by another atom/group of atoms.
Nucleophilic substitution reaction − where a nucleophile substitutes a group or an atom.
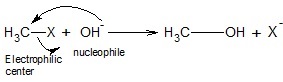
CH3 − X acts as the electrophilic center due to the polarity of C − X bond resulting in δ+ charge on carbon.
OH- acts as the nucleophile attacking the electrophilic carbon. Result is a substituted product. X is replaced by OH group.
Another example: CH3CH2Br+: CN− → CH3CH2CN + Br−
Electrophilic substitution reaction − An electrophile displaces a group or an atom. For example, the given reaction involves the attack of an electrophile NO2+ (nitronium ion).
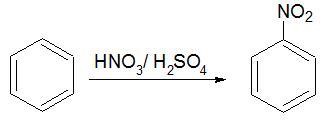
Free radical substitution reaction − The attacking species is a free radical For example, chlorination of alkanes in the presence of UV light involves the attack of chlorine free radicals (Cl.).